Children born with IUGR develop choices of the metabolic syndrome and exhibit deranged markers of hepatorenal physiology.
Metabolic and hepatorenal biochemistry and the rs9939609 FTO polymorphism had been investigated in prepubertal children born with IUGR.
Ninety-eight prepubertal children (46 IUGR and 52 AGA), subdivided in <5 years=”” and=””>>5 years outdated groups had been included. Anthropometry; creatinine, eGFR, urea, AST, ALT, triglycerides, uric acid, complete ldl ldl cholesterol, HDL-c, LDL-c, glucose, C-peptide, insulin and glucagon z-scores; HOMA-IR; leptin and adiponectin concentrations; rs9939609 FTO polymorphism frequency had been measured.
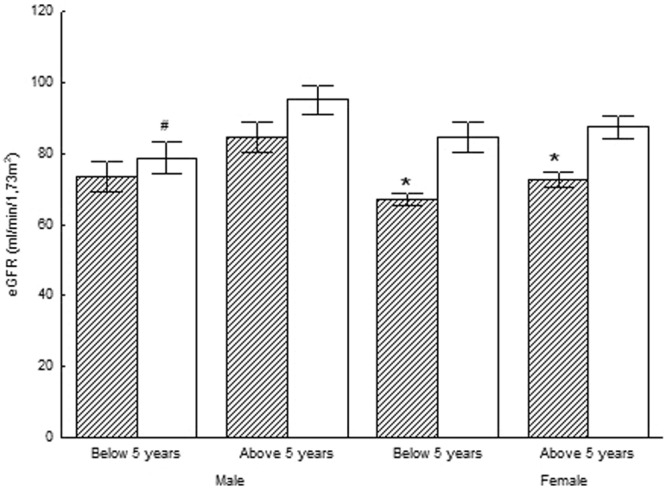
In males, weight and ALT had been bigger and adiponectin was lower, in IUGR < 5 years; C-peptide, insulin and leptin had been bigger in IUGR>> 5 years; C-peptide was bigger in all IUGR, than the respective AGA. In females, creatinine and triglycerides had been bigger in IUGR < 5 years outdated; creatinine was bigger and eGFR was lower in all IUGR, than the respective AGA.
In males and females, creatinine was bigger in all IUGR, than the respective AGA; C-peptide, insulin and HOMA-IR had been lower, and AST was bigger in IUGR < 5 than in IUGR>> 5 years outdated. FTO rs9939609 frequency did not differ between IUGR and AGA.
In conclusion prepubertal males born with IUGR elevated weight, insulin and leptin and decreased adiponectin, as in comparability with males born AGA, emerge as early metabolic syndrome traits. The concentrations of these hormones do not differ between prepubertal males and females born with IUGR. Weight administration, healthful weight loss program and bodily practice must be advisable to these children.
The deranged renal (notably evident in females beneath the age of 5) and liver biochemistry in prepubertal children born with IUGR implies that hepatorenal derangements might begin in utero. Regular checkup of biochemical and lipid profile is advisable for all children born with IUGR.
Chronic Exposure to Sodium Fluoride Triggers Oxidative Biochemistry Misbalance in Mice: Effects on Peripheral Blood Circulation.
The excessive fluoride (F) publicity is said with hurt to cell processes of varied tissue varieties, on account of changes in enzymatic metabolism and breakdown of redox stability. However, few analysis think about doses of F acceptable with human consumption.
Thus, this look at evaluated the implications of persistent publicity to sodium fluoride (NaF) on peripheral blood of mice from the evaluation of biochemical parameters. The animals had been divided into three groups (n = 10) and obtained three concentrations of NaF in the consuming water for 60 days: zero mg/L F, 10 mg/L F, and 50 mg/L F.
The blood was then collected for trolox equal antioxidant functionality (TEAC), thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), concentrations of nitric oxide (NO), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and lowered glutathione (GSH).
The outcomes confirmed that doses of 10 mg/L F and 50 mg/L F had been able to enhance TBARS focus and decrease NO ranges and CAT train in the blood, nevertheless there was no statistical distinction for SOD ranges.
The 50 mg/L F group confirmed an increase in TEAC ranges and a decrease in the GSH content material materials when in comparability with the administration group. In this fashion, oxidative changes in blood from persistent publicity to F, notably on the best dose, level out that F may be a toxic agent and, as a result of this truth, the long-term publicity to excessive doses must be averted.
